-
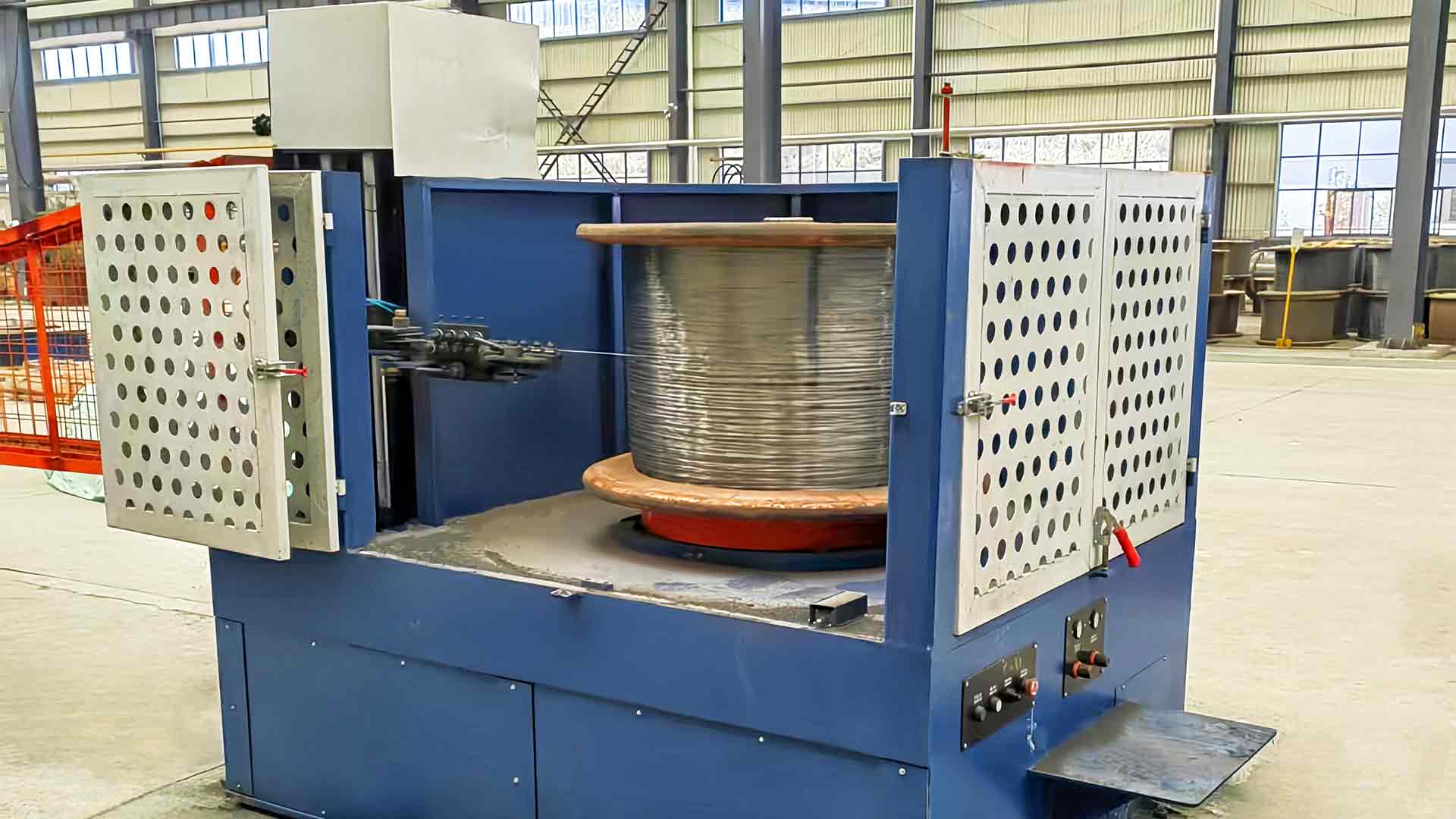
Precision Tension Control Systems: The core mechanism to prevent wire breakage is the precision tension control system, which continuously monitors and regulates the tensile force applied to the wire throughout the drawing process. High-speed operations can generate sudden fluctuations in tension due to variations in wire diameter, material inconsistencies, or die wear. Advanced systems employ load cells, tension sensors, and feedback loops that instantly adjust capstan speed or feed rate to maintain optimal tension. By keeping the wire within its elastic limit, the system ensures uniform stretching, avoids stress concentration points, and prevents snapping, while also maintaining consistent diameter and surface quality. This automated control reduces operator error and allows reliable high-speed production across various wire materials.
-
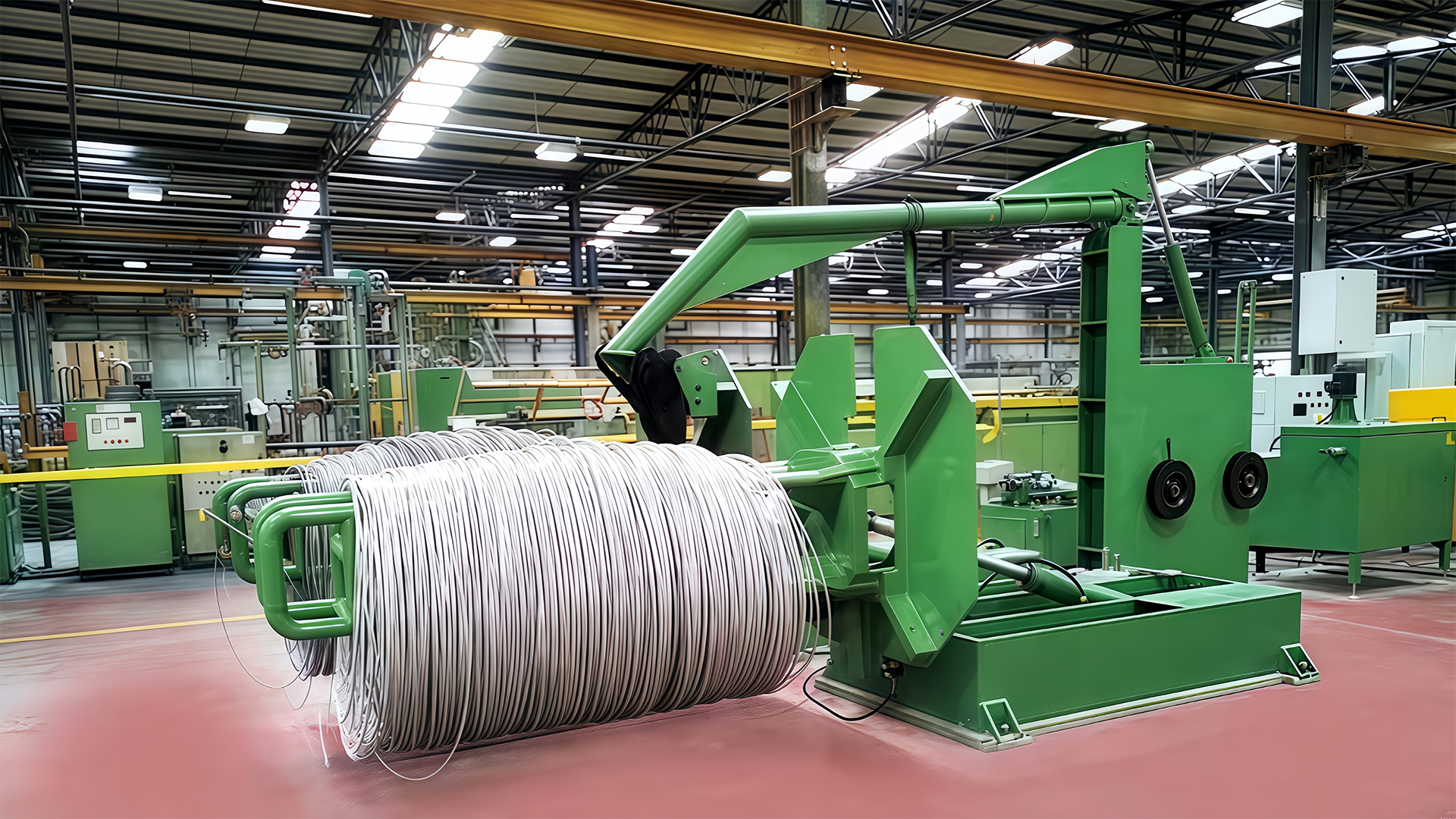
Multi-Stage Drawing with Controlled Reduction: Inverted Wire Drawing Machines commonly employ multi-stage or tandem drawing processes, where the wire passes through a series of dies, each progressively reducing the diameter in controlled increments. The reduction ratio at each stage is carefully calculated based on the wire’s material properties, tensile strength, and ductility limits. Distributing deformation across multiple stages prevents overstraining the wire in a single die, which could lead to micro-cracks, necking, or surface defects. By combining controlled reduction ratios with properly aligned dies, the machine achieves a uniform final diameter while minimizing the risk of deformation or catastrophic breakage, especially during continuous, high-speed production.
-
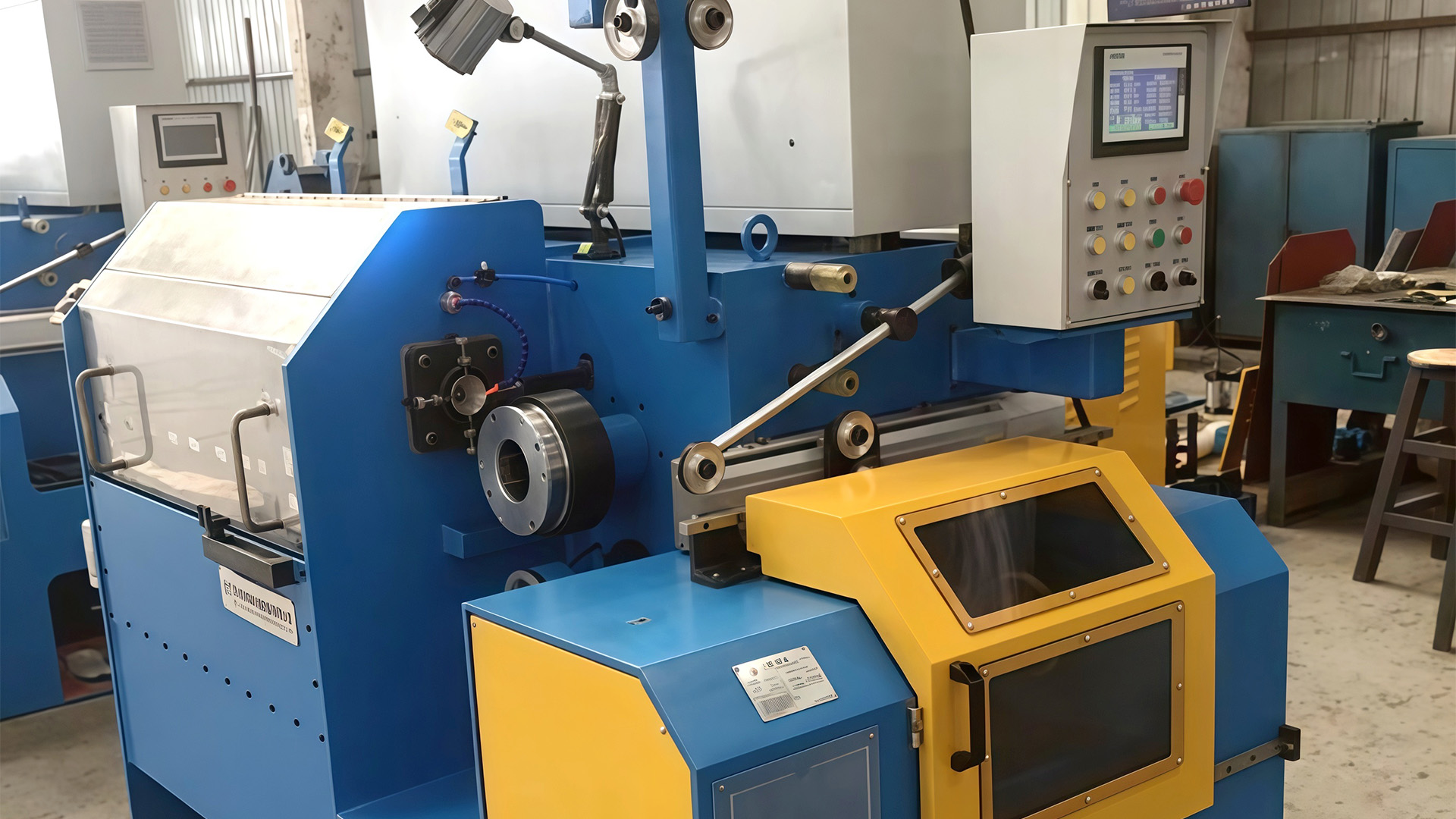
Die Alignment and Precision Guiding Systems: Misalignment during drawing introduces lateral stress and uneven stretching, which can cause surface scratches, ovalization, or breakage. Inverted Wire Drawing Machines feature precision die holders, adjustable alignment guides, and roller systems that maintain the wire perfectly centered throughout each stage. High-precision guiding ensures consistent contact between the wire and die, minimizes frictional wear, and distributes mechanical stress evenly. These alignment mechanisms are essential for processing hard or brittle materials, multi-strand wires, and coated wires, guaranteeing both dimensional accuracy and structural integrity.
-
Automated Speed Synchronization: High-speed wire drawing requires precise coordination between the pay-off reel, capstan rollers, and take-up system. Inverted Wire Drawing Machines employ servo-controlled or electronically synchronized drives to maintain uniform wire speed across all stages. This prevents shock loading, which could occur if the wire accelerates or decelerates too quickly between dies. The synchronization system dynamically adjusts speeds based on real-time feedback from tension and diameter sensors, ensuring smooth and consistent operation. This reduces the likelihood of micro-fractures, stretching beyond elastic limits, and deformation, especially in long continuous runs or high-throughput industrial environments.
-
Integrated Cooling and Lubrication Systems: Friction and heat generated during wire drawing can reduce ductility and increase the likelihood of breakage or surface defects. To mitigate these effects, Inverted Wire Drawing Machines incorporate precisely controlled cooling and lubrication systems, delivering lubricants such as oil or water-based solutions at the wire-die interface. Lubrication reduces friction, while cooling prevents localized thermal softening, preserving mechanical properties. For multi-layered or coated wires, the system can adjust lubricant flow to ensure even coverage without contaminating surfaces, maintaining dimensional accuracy and a defect-free finish. Properly tuned cooling and lubrication are crucial for high-speed operation and tool longevity.
-
Real-Time Monitoring and Feedback Systems: Advanced machines utilize real-time monitoring of tension, diameter, and surface quality to detect anomalies that could lead to wire breakage or deformation. Sensors and digital readouts track mechanical stress, feed speed, and material consistency throughout the process. If deviations are detected—such as excessive tension, misalignment, or irregular diameter—the machine can automatically slow down, adjust capstan speeds, or halt operations. This proactive feedback loop ensures that corrective actions are taken immediately, preventing permanent defects or catastrophic wire failure and improving overall production quality.
-
Overload Protection and Emergency Stops: Safety and wire integrity are further protected by mechanical or electronic overload protection systems, which disengage the drive or shut down the machine if the tensile load exceeds the material’s strength limit. Emergency stop mechanisms are strategically placed to allow operators to immediately halt the process in case of unexpected wire behavior or equipment malfunction. These features safeguard both the wire and the machine, reducing the risk of expensive wire wastage, downtime, and potential operator injury in industrial environments.
-
Material-Specific Operational Parameters: To optimize performance, Inverted Wire Drawing Machines can be programmed with customized parameters for different wire materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, copper, aluminum, or specialty alloys. These settings adjust tension, reduction ratios, speed, and lubrication based on the wire’s ductility, hardness, and tensile strength. By tailoring the process to the specific material, the machine prevents overstressing, surface cracking, or deformation, ensuring high-quality output even under high-speed production conditions. This adaptability is particularly valuable in facilities producing a variety of wire types or grades.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى