Mechanical Design and Wire Path
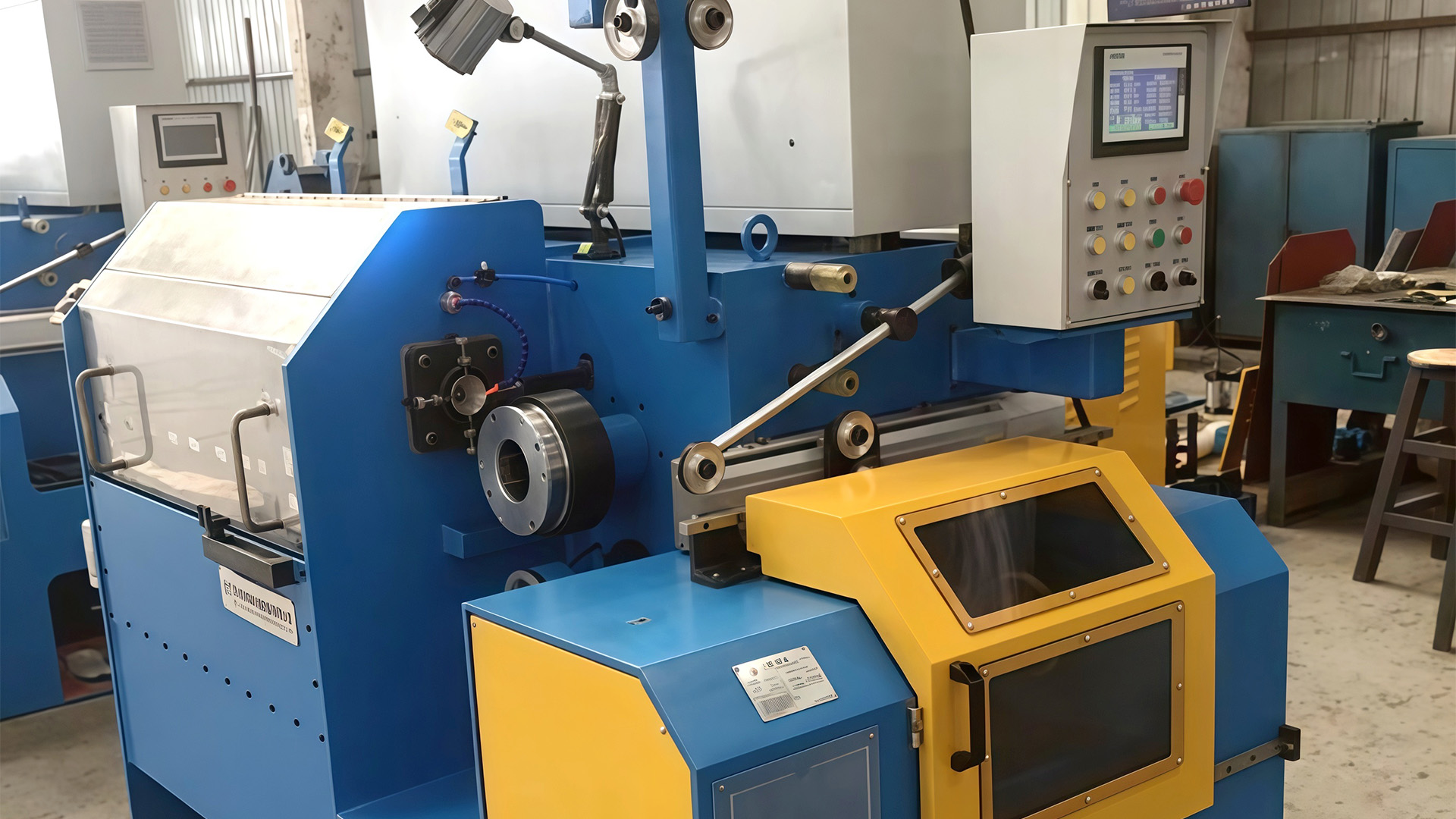
The inverted configuration of the Inverted Wire Drawing Machine is specifically engineered to provide a controlled and smooth wire path, which plays a crucial role in tension management. Wire guides, rollers, and capstans are positioned strategically to ensure that the wire moves in a linear and minimally stressed trajectory, avoiding sharp bends or abrupt directional changes that could concentrate stress and lead to breakage. The inverted layout also facilitates a gradual application of tensile forces, allowing the wire to undergo consistent reduction in diameter without localized deformation. By minimizing friction points and distributing tension evenly along the entire wire length, the mechanical design of the machine helps maintain wire integrity and uniformity, even during high-speed or high-volume operations.
Controlled Drawing Force
Effective tension management in the Inverted Wire Drawing Machine relies heavily on precise control of the drawing force applied by the dies. High-precision motors, often servo-driven, regulate the speed at which the wire is pulled through the dies, ensuring that the tension remains within safe limits. This prevents overstretching, which can cause breakage, and under-tension, which may result in bending or irregular surface finish. The machine synchronizes die resistance with spool rotation, creating a balanced and continuous drawing process. By controlling both the pulling force and feed rate, the machine achieves uniform wire reduction while maintaining dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
Feedback and Tension Monitoring Systems
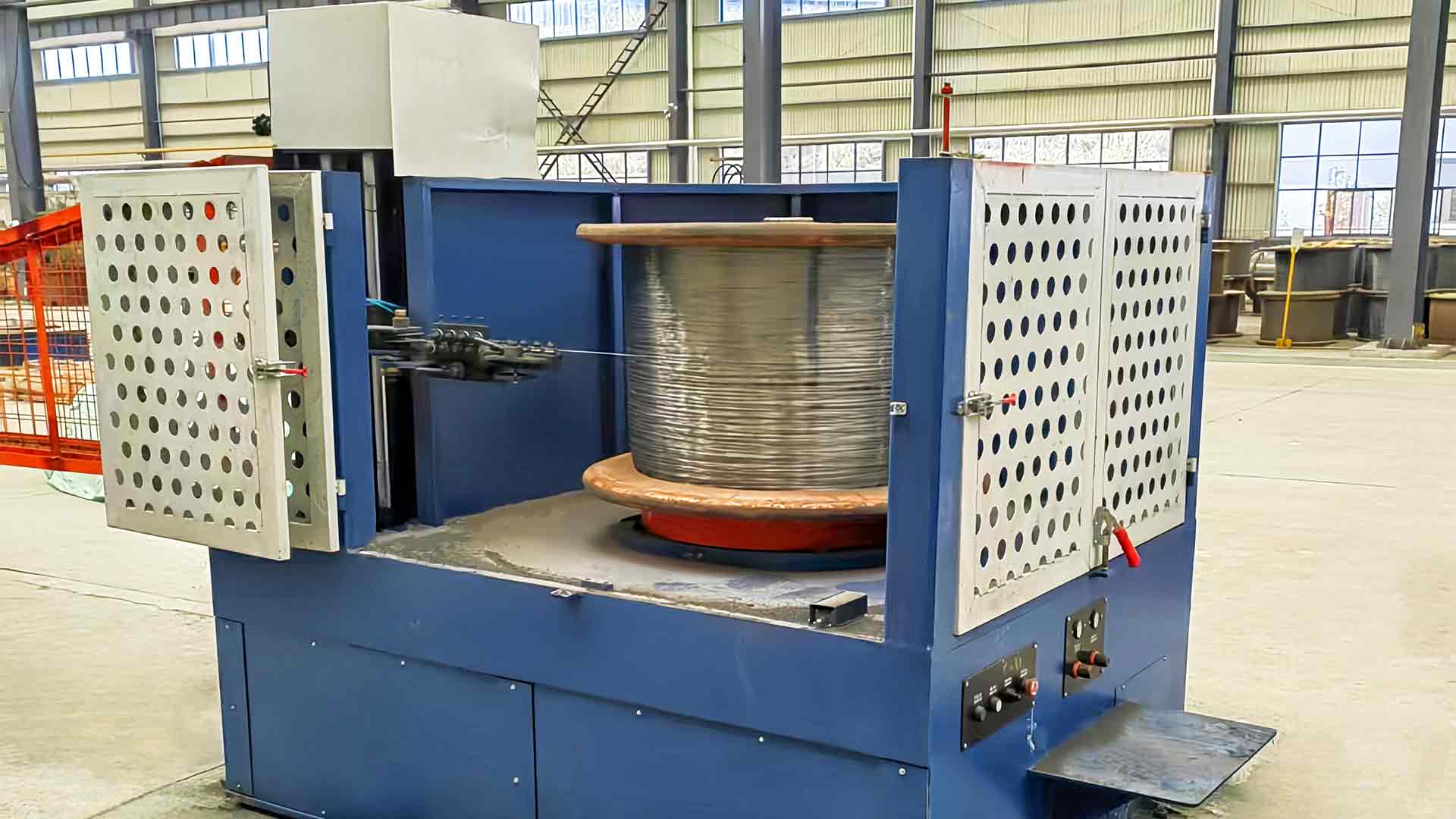
Modern Inverted Wire Drawing Machines incorporate advanced tension monitoring systems that continuously track the tensile load on the wire at multiple points along the machine. These sensors feed data into automated control systems, which adjust spool speed, die resistance, or drawing rate in real-time to maintain consistent tension. If the system detects a spike or drop in tension beyond predefined thresholds, it can make instantaneous corrections, preventing wire breakage or permanent deformation. In addition, tension data can be recorded for quality assurance purposes, enabling operators to analyze and optimize the drawing process, ensuring that each batch of wire meets strict industrial specifications.
Lubrication and Surface Interaction
Proper lubrication is an integral part of tension management in the Inverted Wire Drawing Machine. Automated lubrication systems supply a consistent layer of drawing oil or grease between the wire and dies, significantly reducing friction and heat generation during the drawing process. Lower friction allows the wire to slide smoothly through the dies, minimizing sudden tension spikes that could lead to breakage or surface defects. Effective lubrication also protects the die surfaces from wear, further stabilizing the tension control process and ensuring long-term reliability of both the machine and the wire product. This careful balance of mechanical force and lubrication is essential for maintaining high-quality wire output.
Accommodation for Material Variability
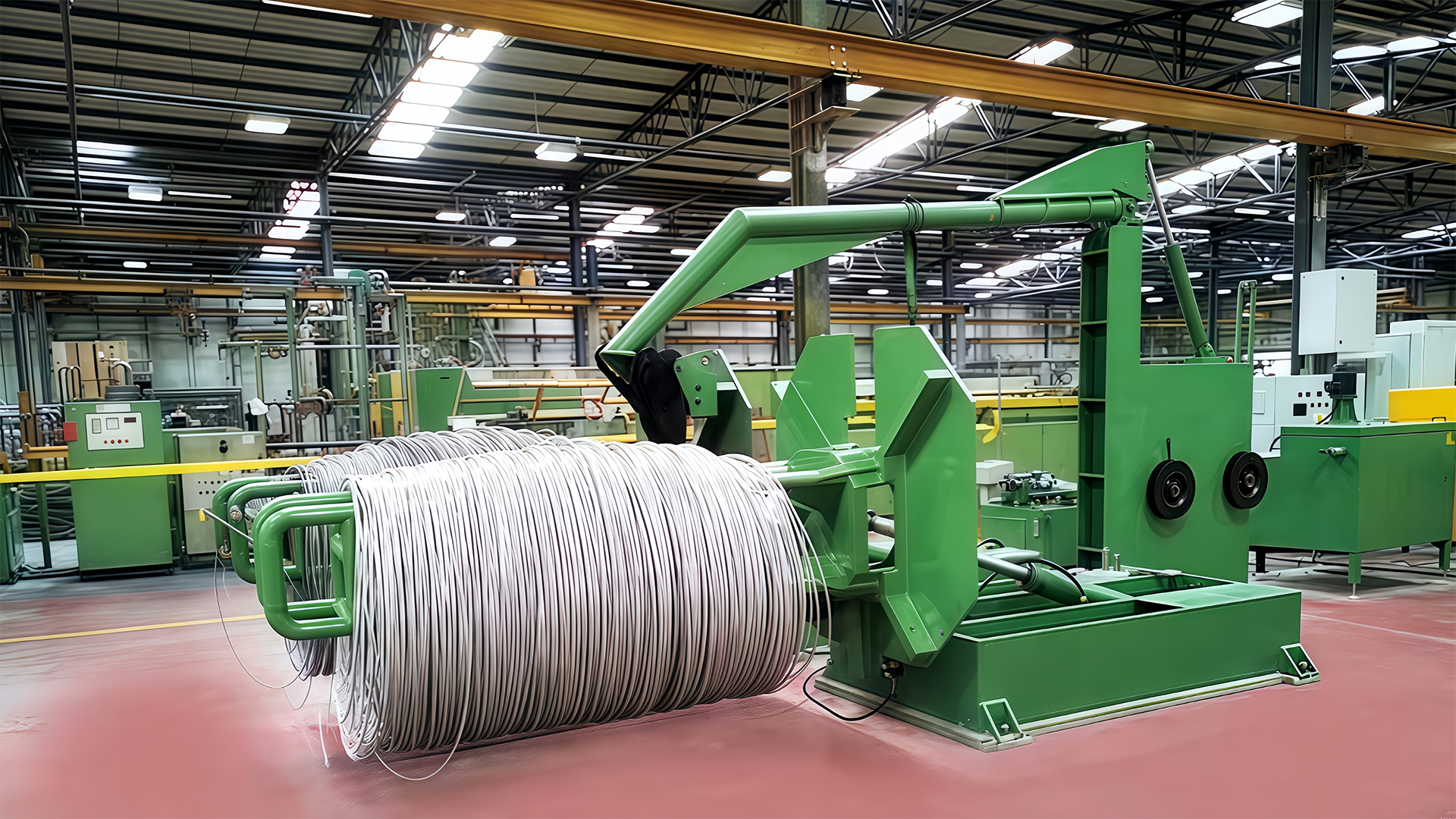
The Inverted Wire Drawing Machine is designed to handle a wide range of metals and alloys, each with unique tensile strengths, ductility, and surface properties. To maintain optimal tension, operators can configure the machine’s settings to match the specific characteristics of the wire being drawn. This includes adjusting pulling speed, die pressure, and lubrication levels to accommodate differences in material behavior. During multi-pass drawing sequences, the machine can dynamically modify tension for each stage, ensuring that the wire is consistently reduced without overstressing or deforming. This adaptability allows the machine to produce high-precision wires with uniform diameter, smooth surface finish, and structural integrity, regardless of material type.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى